1. What is Windows Autopatch?
Windows Autopatch is a cloud service that automatically keeps your Windows devices, Microsoft 365 Apps, Edge, and Teams up to date. It helps improve security and productivity by ensuring your organization always has the latest updates without manual effort.
2. Prerequisites:
1. I am using the following licenses in my environment.
2. You need the Microsoft Entra Global Administrator role to activate Windows Autopatch features. To register devices, manage update deployments, and perform reporting tasks, you need the Intune Administrator role.
3. Keep the Microsoft Entra groups (Assigned/Dynamic Device) ready before starting with Windows Autopatch so they can be used during the Update Ring configuration.
3. URLs:
In the production environment, ensure that the required URLs and ports for Windows Autopatch are enabled.
4. Activate Windows Autopatch features:
1. Navigate to the Microsoft Intune admin center https://intune.microsoft.com/
2. In the left pane, select Tenant Administration > Windows Autopatch > Feature Activate.
3. The Features are activated successfully.
4. You now have access to additional features under the Windows Autopatch tab.
5. Add Admin Contacts:
The Admin Contacts tab is used to manage and configure the list of IT administrators responsible for receiving critical updates and notifications related to Autopatch operations.
1. Go to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
2. Select Tenant administration from the left navigation menu. Under the Windows Autopatch section, select Admin Contacts. Click Add. Provide the appropriate details. Click Save.
6. Create an Autopatch group:
An Autopatch group is a logical container or unit that groups several Microsoft Entra groups, and software update policies, such as Update rings policy for Windows 10 and later and feature updates policy for Windows 10 and later policies.
- Go to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
- Select Tenant administration from the left navigation menu. Under the Windows Autopatch section, select Autopatch groups. In the Autopatch groups blade, select Create.
1. Under the Basics tab, provide a suitable name. Click Next.
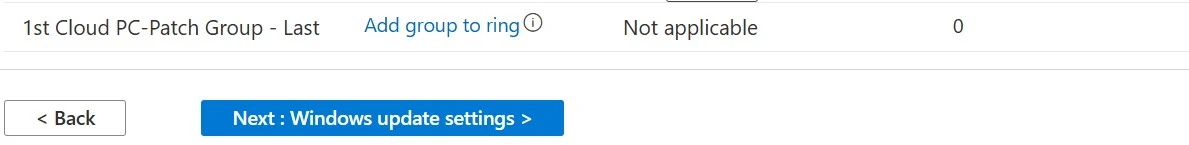
2. Under the Deployment rings tab, there are two default rings: Test and Last deployment rings
- Both the Test and Last deployment rings can't be removed or renamed from Autopatch groups.
- The Test and Last deployment rings support only a single Microsoft Entra group.
- If you don't add more deployment rings, the Test deployment ring can be used as the pilot deployment ring, and the Last deployment ring can be used as the production deployment ring.
There are 2 distribution types: Dynamic distribution group and Assigned distribution group
2.1. Dynamic distribution group:
- You can add one more Microsoft Entra group, either dynamic or assigned, based on devices.
- You can distribute devices across several deployment rings based on percentage values, which can be customized.
- The Dynamic distribution group is not applicable to the Test and Last deployment rings.
1. Click on 'Add groups' next to 'Dynamic group distribution'.
2.2. Assigned Distribution Group:2. You can add one more Microsoft Entra group, either dynamic or assigned, based on devices.
3. Click Select.
4. The selected groups (IT-CloudPC-Devices, HR-CloudPC-Devices) is reflecting under Dynamic group distribution.
5. You can click on '+Add deployment ring' and create the appropriate number of rings based on the requirements. For this demo, we have created two rings.
6. You can either click 'Apply default dynamic group distribution' or manually add a percentage corresponding to Ring 1 and Ring 2, ensuring the total adds up to 100%.
- To each ring, you can add a single Microsoft Entra group, either dynamic or assigned, based on devices.
2. Once the groups are added, click 'Next: Windows update settings'
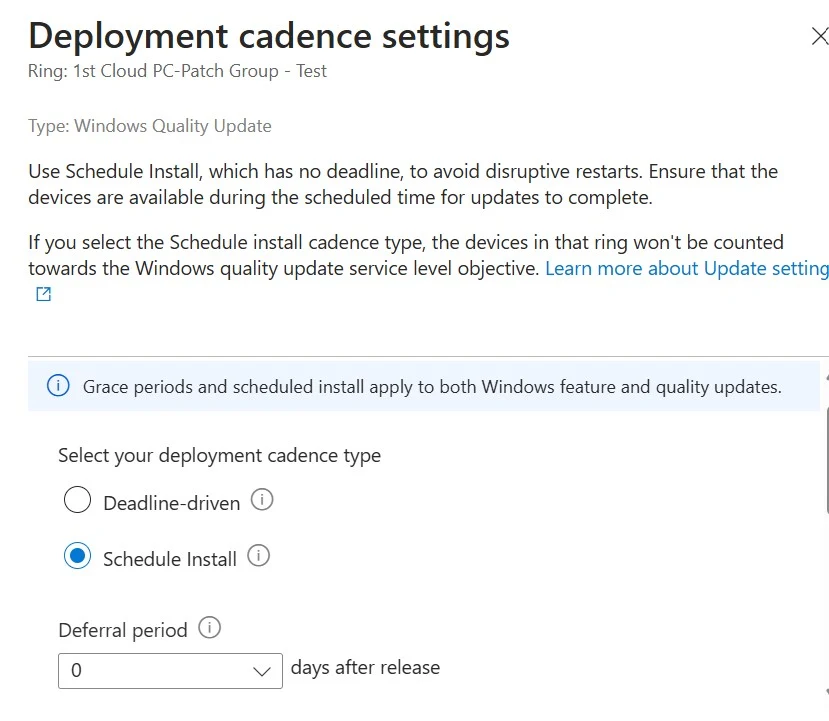
3. Under the Windows Update settings tab, there are two Cadence types. The default one you see is Deadline-driven, and the other is Schedule Install.
4. The number of days displayed below are the default values assigned by the system. You can customize them based on your requirements.
5. For E.g, Click on the 3 vertical dots corresponding to the Test ring.
6. Click Manage deployment cadence.
7. Deadline-Driven:- Updates become available to devices during the specified time range. Devices can be updated at any point in that window.
- You can control and customize the deferral, deadline, and grace period based on your business needs and organizational requirements.
- Each deployment ring can be scheduled independently, with no dependencies on the previous deployment ring.
- The cadence cannot be changed for a ring during an ongoing update cycle.
8. Schedule Install:
- Updates are only installed during the specified time window. Best for business-critical devices only.
- Minimizes disruptions by preventing forced restarts.
- Devices will only update and restart according to the specified time.
- Scheduled Install has two options:
8.2. Schedule Install and Restart – Installs updates and restarts at a scheduled time.
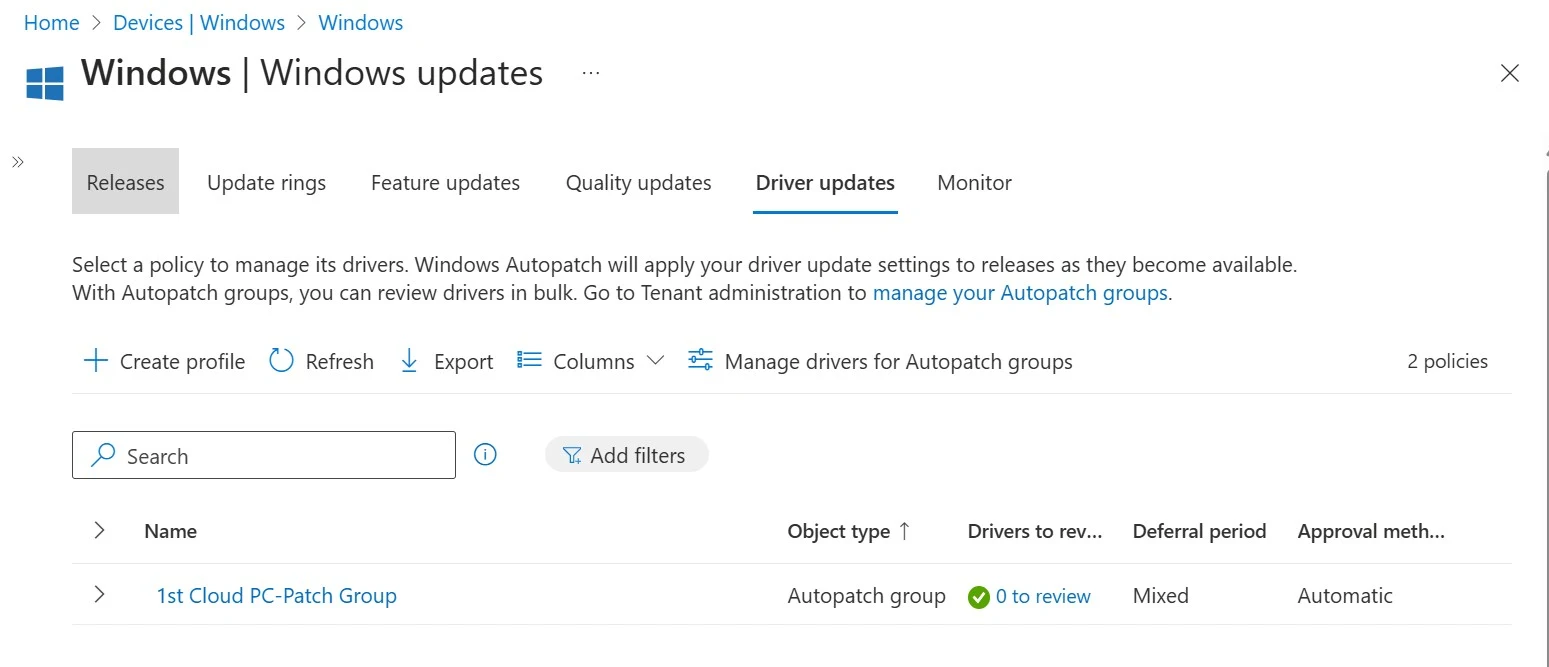
10. Under Driver update settings, the default option selected is Allow - Create driver policies for this Autopatch group.
11. You can change the approval method to either Automatic or Manual. By default, it is set to Automatic.
12. Click Next: Review +Create.
14. Autopatch group is created.
7. Update Settings:
1. Navigate to Tenant Administration>>Windows Autopatch>>Autopatch groups>>Update settings.
Here, you have options such as Expedited quality updates, Microsoft 365 Apps updates, and Edge updates. You can toggle the switch to Allow automatic updates.

8. Windows Updates:
Go to Devices-Manage Updates-Windows Updates-Update rings
1. Releases:
You can view the details of Quality and Feature Updates.
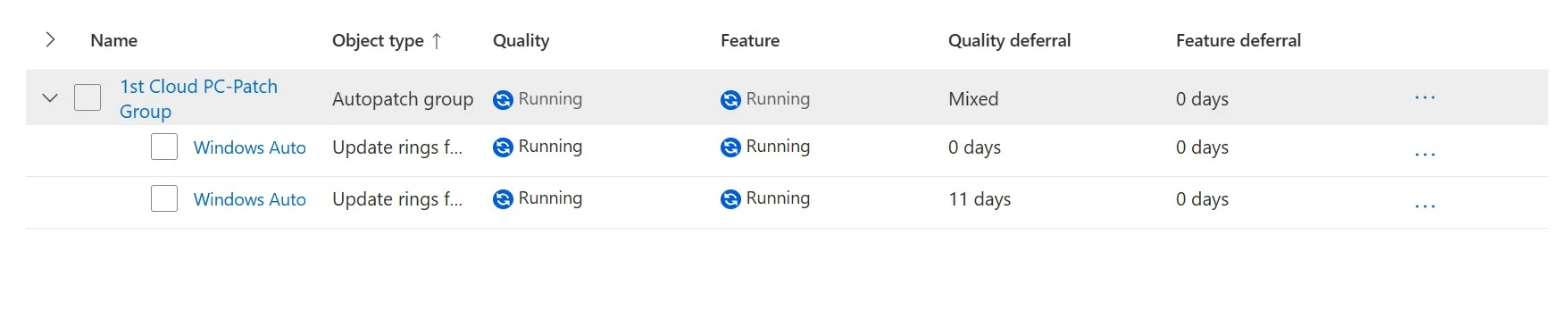
2. Update rings:
3. Feature Updates:
- Windows Autopatch - Global DSS Policy allows eligible devices to benefit from the standard automatic update channel. It provides tools for controlled rollouts of annual Windows feature updates, including version targeting and phased releases.
- If you’re ahead of the current minimum OS version enforced by Windows Autopatch in your organization, you can edit Windows Autopatch’s default Windows feature update policy and select your desired targeted version.
4. Driver Updates:


































Comments
Post a Comment