1. What is Implicit and Explicit Outbound Internet Access?
Explicit outbound internet access includes:
1. Virtual Machines created in a subnet associated to a NAT gateway.
2. Virtual Machines deployed in the backend pool of a basic public load balancer or standard load balancer with outbound rules defines.
3. Virtual machines with public IP addresses.
Virtual Machines that do not have one of the explicit ways of outbound internet access as mentioned above, Microsoft assigns default outbound public IP address. This access is referred to as default outbound access.
2. What is the impact of this Announcement?
Starting September 30th, 2025, the default outbound access to the internet will be stopped for the new deployments in Azure. Existing VMs will not be impacted by this retirement.
However, Microsoft also says that the implicit IP addresses it provides for the outbound internet access may change and should not be relied upon for production workloads.
3. Best Practice:
You need to explicitly provide outbound internet access to the subnets for your workload requirements. Microsoft recommends using a NAT gateway for explicit outbound connectivity.
4. Considerations:
1. Once you enable the Private Subnet option for the subnet, the change cannot be reverted.
2. When using Azure Firewall with a NAT gateway, the firewall should be deployed in a specific availability zone.
3. When Azure Firewall is deployed in an availability zone, the Public IP associated with the Firewall should also be deployed in an availability zone.
4. In an AVD environment, we typically use a Hub and Spoke network topology along with Azure Firewall. In this scenario, we will integrate the NAT Gateway with Azure Firewall for outbound connectivity.
5. Enable Private Subnet feature for Spoke Subnet:
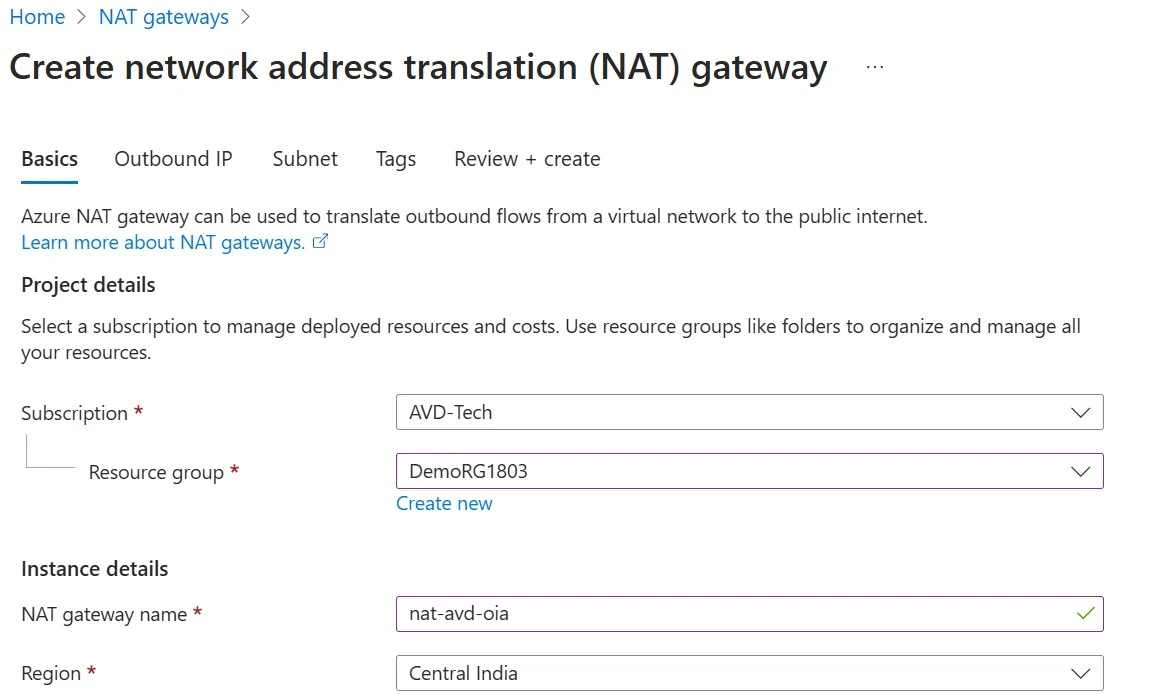
6. Create a NAT Gateway:
11. Under Virtual Network, select the Hub Vnet.













Comments
Post a Comment